We assume as an example automaton the automaton 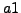 in figure 5.5.6 from above along with the execution graph related to
in figure 5.5.6 from above along with the execution graph related to 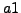 in figure 5.3.
in figure 5.3.
Some examples of CTL-formula and their interpretation relativ to 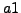 :
:
-
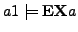 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 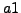 there is a run
there is a run
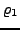 as a path
as a path 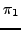 where at position i= 0+1 = 1 is the state
where at position i= 0+1 = 1 is the state 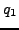 with property
with property 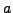 which follows state
which follows state 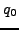 with property
with property 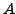 */
*/
-
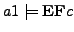 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 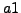 there is a run
there is a run
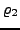 as a path
as a path 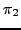 where at position i= 2 is the state
where at position i= 2 is the state 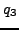 with property
with property 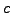 */
*/
-
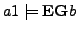 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 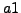 there is a run
there is a run
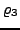 as a path
as a path 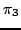 where on all positions there is a state with property
where on all positions there is a state with property 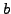 ; this is the path
; this is the path
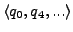 */
*/
-
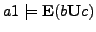 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 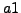 there is a run
there is a run
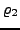 as a path
as a path 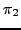 and in this run there is the state
and in this run there is the state 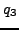 at position i=2 with property
at position i=2 with property 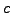 and at positions 1-2 are the states
and at positions 1-2 are the states
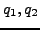 with property
with property 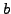 */
*/
-
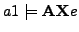 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 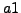 it holds for paths at positions i= 0+1 = 1 that there are states
it holds for paths at positions i= 0+1 = 1 that there are states
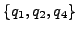 with property
with property 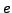 which are following state
which are following state 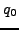 */
*/
-
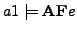 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 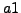 it holds for all paths at positions i= 0+1 = 1 that there are states
it holds for all paths at positions i= 0+1 = 1 that there are states
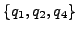 with property
with property 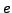 which are following state
which are following state 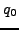 */
*/
-
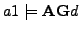 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 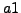 it holds for all paths at all positions that there are states with property
it holds for all paths at all positions that there are states with property 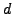 */
*/
-
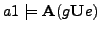 /* In the execution graph of
/* In the execution graph of 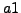 it holds for all paths that there are positions whose states hold property
it holds for all paths that there are positions whose states hold property 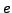 and these states are successors of states which have the property g */
and these states are successors of states which have the property g */
Gerd Doeben-Henisch
2010-03-03
![]() in figure 5.5.6 from above along with the execution graph related to
in figure 5.5.6 from above along with the execution graph related to ![]() in figure 5.3.
in figure 5.3.
![]() :
: